代码:https://github.com/felicityin/cuda-demo/blob/main/cuda/matrix_transpose.cu
本文使用笛卡尔坐标系 (x, y),threadIdx.x 为水平方向,threadIdx.y 为垂直方向,这是为了确保访存连续(memory coalescing)。我们需要将变化最快的分量映射到内存中的连续元素,threadIdx.x 和 blockIdx.x 分别在 block 和 grid 内变化最快。
in:
b00 b01 b02 | b03 b04 b05 | b06 b07 b08
b10 b11 b12 | b13 b14 b15 | b16 b17 b18
b20 b21 b22 | b23 b24 b25 | b26 b27 b28
------------+-------------+------------
b30 b31 b32 | b33 b34 b35 | b36 b37 b38
b40 b41 b41 | b43 b44 b45 | b46 b47 b48
b50 b51 b52 | b53 b54 b55 | b56 b57 b58
out:
b00 b10 b20 | b30 b40 b50
b01 b11 b21 | b31 b41 b51
b02 b12 b22 | b32 b42 b52
------------+------------
b03 b13 b23 | b33 b43 b53
b04 b14 b24 | b34 b44 b54
b05 b15 b25 | b35 b45 b55
------------+------------
b06 b16 b26 | b36 b46 b56
b07 b17 b27 | b37 b47 b57
b08 b18 b28 | b38 b48 b58 简单的矩阵转置
内核启动的线程块 block 包含 32 * 32 个线程(代码中 TILE_DIM=32)。每个线程块 block 转置一个 32 * 32 的子矩阵块,其中的每个线程转置 1 个元素。
__global__ void transposeNaive(int *output, const int *input, int width, int height) {
int col = blockIdx.x * TILE_DIM + threadIdx.x;
int row = blockIdx.y * TILE_DIM + threadIdx.y;
size_t len = width * height;
size_t idx_in = row * width + col;
size_t idx_out = col * height + row;
if (idx_in < len && idx_out < len) {
output[idx_out] = input[idx_in];
}
}dim3 dimBlock(TILE_DIM, TILE_DIM);
dim3 dimGrid((width + TILE_DIM - 1) / TILE_DIM, (height + TILE_DIM - 1) / TILE_DIM);
transposeNaive<<<dimGrid, dimBlock>>>(d_output, d_input, width, height);增加每个线程的工作量
内核启动的线程块 block 包含 32 * 8 个线程(代码中 TILE_DIM=32,BLOCK_ROWS=8)。每个线程块 block 转置一个 32 * 32 的子矩阵块,其中的每个线程转置 4 个元素。
__global__ void transposeNaiveV2(int *output, const int *input, int width, int height) {
int col = blockIdx.x * TILE_DIM + threadIdx.x;
int row = blockIdx.y * TILE_DIM + threadIdx.y;
size_t len = width * height;
for (int j = 0; j < TILE_DIM; j += BLOCK_ROWS) {
size_t idx_in = (row + j) * width + col;
size_t idx_out = col * height + row + j;
if (idx_in < len && idx_out < len) {
output[idx_out] = input[idx_in];
}
}
}dim3 blockSize(TILE_DIM, BLOCK_ROWS);
dim3 gridSize((width + TILE_DIM - 1) / TILE_DIM, (height + TILE_DIM - 1) / TILE_DIM);
transposeNaiveV2<<<gridSize, blockSize>>>(d_output, d_input, width, height);读数据时访存连续,但是写数据时相邻线程间的访存不连续,会导致性能较低。
使用 shared memory 实现合并访存
访存过程:(kernel <---> global) <---> (L1 <---> L2 <---> Device Memory)
合并访存:L2 到 L1 每次传输的最小数据量是 32 byte(一个 sector),即使只需要 1 个 byte。如果 warp 内的线程访问的地址连续,则传输的次数最少。若一个线程束对全局内存的一次访问导致最少的数据传输,则称该访问为合并访存,否则为非合并访存。
可以先将 input 中的行数据写入 shared memory,然后将 shared memory 中的列数据写入 output。因为 shared memory 的访问速度比 global memory 快,所以读取时访存不连续对性能的影响较小。
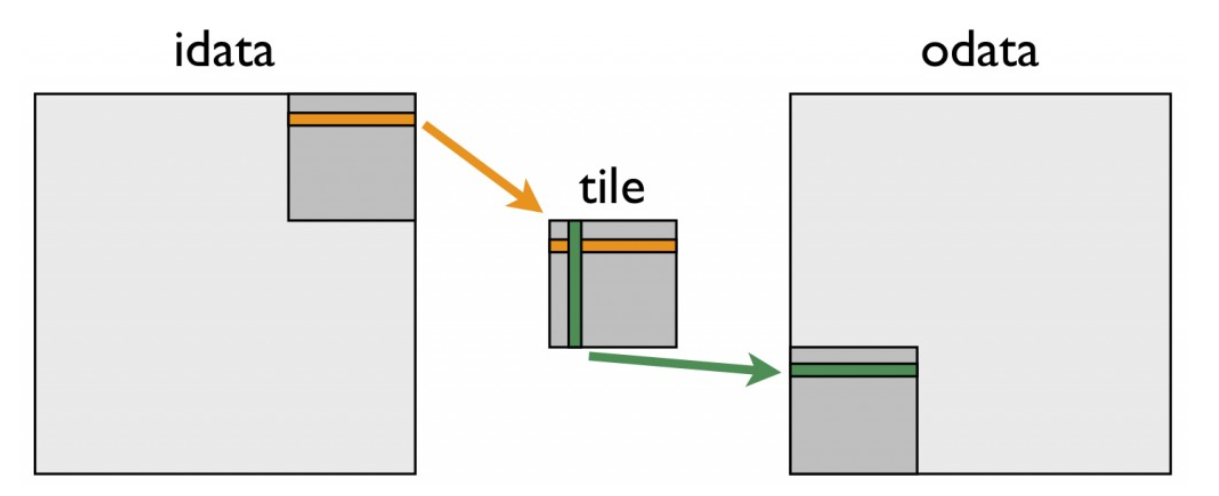
图片来源:An Efficient Matrix Transpose in CUDA C/C++
__global__ void transposeSharedMemory(int *output, const int *input, int width, int height) {
__shared__ int s_mem[TILE_DIM][TILE_DIM+1];
int col = blockIdx.x * TILE_DIM + threadIdx.x;
int row = blockIdx.y * TILE_DIM + threadIdx.y;
size_t len = width * height;
for (int j = 0; j < TILE_DIM; j += BLOCK_ROWS) {
size_t idx_in = (row + j) * width + col;
if (idx_in < len) {
s_mem[threadIdx.y + j][threadIdx.x] = input[idx_in];
}
}
__syncthreads();
col = blockIdx.y * TILE_DIM + threadIdx.x; // transpose block offset
row = blockIdx.x * TILE_DIM + threadIdx.y;
for (int j = 0; j < TILE_DIM; j += BLOCK_ROWS) {
size_t idx_out = (row + j) * height + col;
if (idx_out < len) {
output[idx_out] = s_mem[threadIdx.x][threadIdx.y + j];
}
}
}dim3 blockSize(TILE_DIM, BLOCK_ROWS);
dim3 gridSize((width + TILE_DIM - 1) / TILE_DIM, (height + TILE_DIM - 1) / TILE_DIM);
transposeSharedMemory<<<gridSize, blockSize>>>(d_output, d_input, width, height);第一个循环中,一组线程从 input 中读取连续数据到共享内存 s_mem 中。
重新计算数组索引后(只需要将 block 的坐标转置即可,block 内的坐标不变),将 s_mem 中的一列写入 output 的连续地址。
因为线程写入 output 的数据并非从 input 读取的数据,所以需要块级屏障同步函数 __syncthreads()
在创建共享内存 s_mem 时,宽度多 1,这样可以避免 bank 冲突。对于一个 32 × 32 元素的共享内存块,同一列数据中的所有元素都映射到同一个 bank,这会导致同一个 warp 中的不同线程读取一列数据会引发 32 路 bank 冲突。
但是该实现有一个局限,矩阵高度小于 32 或超过 2^20 次方都会报错。但是 grid 的 x 上限 2^31 高于 y 上限,所以可以尝试使用一维 grid
使用一维 grid 转置更大矩阵
内核启动的线程块 block 包含 32 个线程(代码中 TILE_DIM=32)。每个线程块 block 转置一个 32 * 32 的子矩阵块,其中的每个线程转置 TILE_DIM 个元素。
__global__ void __launch_bounds__(TILE_DIM)
transposeSharedMemoryV2(int *output, const int *input, int width, int height) {
__shared__ int s_mem[TILE_DIM][TILE_DIM + 1];
size_t dim_x = (width + TILE_DIM - 1) / TILE_DIM;
size_t bid = blockIdx.x; // (x, 1, 1)
size_t bid_y = bid / dim_x;
size_t bid_x = bid % dim_x; // (bid_x, bid_y, 1)
size_t tid = threadIdx.x;
size_t idx_in = bid_y * TILE_DIM * width + bid_x * TILE_DIM + tid;
size_t idx_out = bid_x * TILE_DIM * height + bid_y * TILE_DIM + tid;
bool boundray_column = bid_x * TILE_DIM + tid < width;
size_t row_offset = bid_y * TILE_DIM + 0;
for (auto i = 0; i < TILE_DIM; ++i) {
bool boundray = boundray_column && (row_offset + i < height);
s_mem[i][tid] = (boundray) ? input[idx_in + i * width] : 0;
}
__syncthreads();
boundray_column = bid_y * TILE_DIM + tid < height;
row_offset = bid_x * TILE_DIM + 0;
for (auto i = 0; i < TILE_DIM; ++i) {
bool boundray = boundray_column && (row_offset + i < width);
if (boundray)
output[idx_out + i * height] = s_mem[tid][i];
}
}size_t grid_x = (width + TILE_DIM - 1) / TILE_DIM;
size_t grid_y = (height + TILE_DIM - 1) / TILE_DIM;
dim3 grid(grid_x * grid_y);
dim3 block(TILE_DIM);
transposeSharedMemoryV2<<<grid, block>>>(d_output, d_input, width, height);结果
[native] Average time per transpose: 13.520638 ms
[native v2] Average time per transpose: 13.213485 ms
[shared memory] Average time per transpose: 3.634523 ms
[shared memory v2] Average time per transpose: 3.523999 ms


没有评论